Git is included in most modern distributions, but there is still an extra script that is packaged with the git source that we need to use for managing a system image.
-
 Download and install git
Download and install git
-
Directions can be found at http://git-scm.com/download
-
 Download setgitperms.perl
Download setgitperms.perl
-
From git source tree: https://raw.github.com/git/git/master/contrib/hooks/setgitperms.perl
-
 Create a git repository in your system image
Create a git repository in your system image
-
# cd /var/lib/oneSIS/images/oneSIS_image_dir
# git init
-
 Create some hooks to enable tracking permissions/ownership
Create some hooks to enable tracking permissions/ownership
-
# rm -f .git/hooks/*
# cp setgitperms.perl .git/hooks
Create .git/hooks/pre-commit#  /bin/sh
/bin/shSUBDIRECTORY_OK=1 . git-sh-setup $GIT_DIR/hooks/setgitperms.perl -r Create both .git/hooks/post-checkout and .git/hooks/post-merge
#  /bin/sh
/bin/shSUBDIRECTORY_OK=1 . git-sh-setup $GIT_DIR/hooks/setgitperms.perl -w
-
 Git does not track empty directories so make sure that none are empty
Git does not track empty directories so make sure that none are empty
-
Put a .gitignore file in every empty directory
# find . -name .git -prune -o -type d -empty -exec touch {}/.gitignore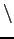 ;
;
-
 Git does not track device files so create a tar archive for them
Git does not track device files so create a tar archive for them
-
# find .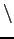 ( -type b -o -type c -o -type p
( -type b -o -type c -o -type p 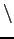 ) -exec tar rf dev/devs.tar {}
) -exec tar rf dev/devs.tar {} 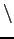 ;
;
-
 Add all files into the git repository
Add all files into the git repository
-
This step may take some time. Be sure to add a useful comment to all commits.
# git add .
# git commit